Introduction:
In the vast world of electrical motors, understanding how the windings and connections work is crucial. In this guide, we will delve into the essential concepts behind motor windings and explore the different ways of connecting them. Whether you are a technology enthusiast or an aspiring engineer, this guide will provide you with valuable insights into the fascinating realm of motor mechanics.
Contents
Motor Windings and Terminal Boxes
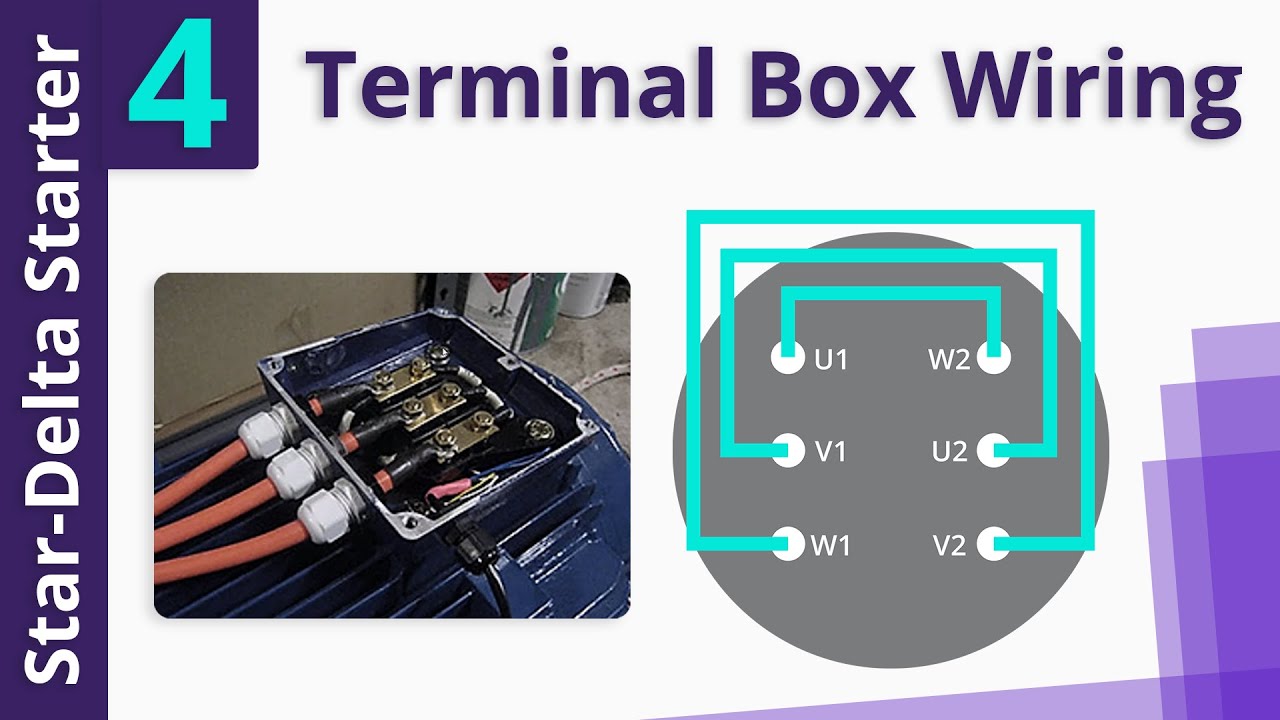
Every electrical motor contains copper windings that play a vital role in its operation. These windings determine the motor’s ability to generate rotational motion when electricity is supplied. To simplify the representation of these windings, we use three symbols: U1, V1, W1 for the upper ends, and U2, V2, W2 for the lower ends.

To locate these winding ends in real-world scenarios, motor designers incorporate a terminal box in every three-phase motor. The terminal box houses the terminals that correspond to the motor windings. Although the arrangement is similar to the winding schematics, there is a slight difference. For instance, while the winding schematics use U2, V2, and W2 for the lower ends, the terminal box may label them as W2, U2, and V2, respectively.
Star and Delta Connections
Understanding the two primary methods of connecting motor windings, known as star and delta connections, is crucial for motor control. In a star connection, the three winding ends are connected together, allowing the motor to start efficiently.

On the other hand, delta connection involves linking specific winding ends in a triangular pattern. This connection is commonly used after the motor gains sufficient speed, as it reduces the current drawn during the startup phase.

Automatic Connection Changing with Contactors
To enable the automatic switching between star and delta connections, contactors play a vital role. By utilizing contactors, it becomes possible to change the motor’s connection without disrupting its operation. This feature is particularly useful for limiting the current draw during the startup phase.
In our upcoming lesson, we will delve into the details of how contactors facilitate the automatic switching of motor windings. Stay tuned for a comprehensive understanding of this essential aspect of motor control.
FAQs
Q: How do I locate the winding ends on a three-phase motor?
A: Look for the terminal box, where the winding ends are represented as terminals.
Q: What is the difference between the winding schematics and the labels on the terminal box?
A: The lower ends may be labeled differently on the terminal box compared to the winding schematics. For example, U2, V2, and W2 in the schematics may be labeled as W2, U2, and V2 on the terminal box.
Q: Why is it necessary to start the motor in star connection before switching to delta?
A: Starting the motor in star connection helps limit the current draw during the startup phase, ensuring a smooth transition to the delta connection.
Q: How can contactors facilitate automatic connection changing?
A: Contactors are used to automate the process of changing the motor’s connection, allowing for seamless transitions between star and delta configurations.
Conclusion
Understanding motor windings and their connections is pivotal for anyone seeking a comprehensive understanding of electrical motors. By grasping the concepts behind star and delta connections, as well as the role of contactors, you can gain the knowledge necessary to control these motors effectively. Stay tuned for our next lesson, where we will explore the intricacies of contactor-based connection switching. For more engaging content and insightful guides on technology, visit Techal.


