Curved rails are a crucial component of architectural structures, offering both functionality and aesthetics. In this article, we will dive deep into the process of designing curved rails using sketches and solid modeling in Chapter 3D. Join us as we explore the steps involved in creating a hand-rolled rail system along a street and learn how to make the most of the sketching and drafting tools at your disposal.
Contents
Planning the Design
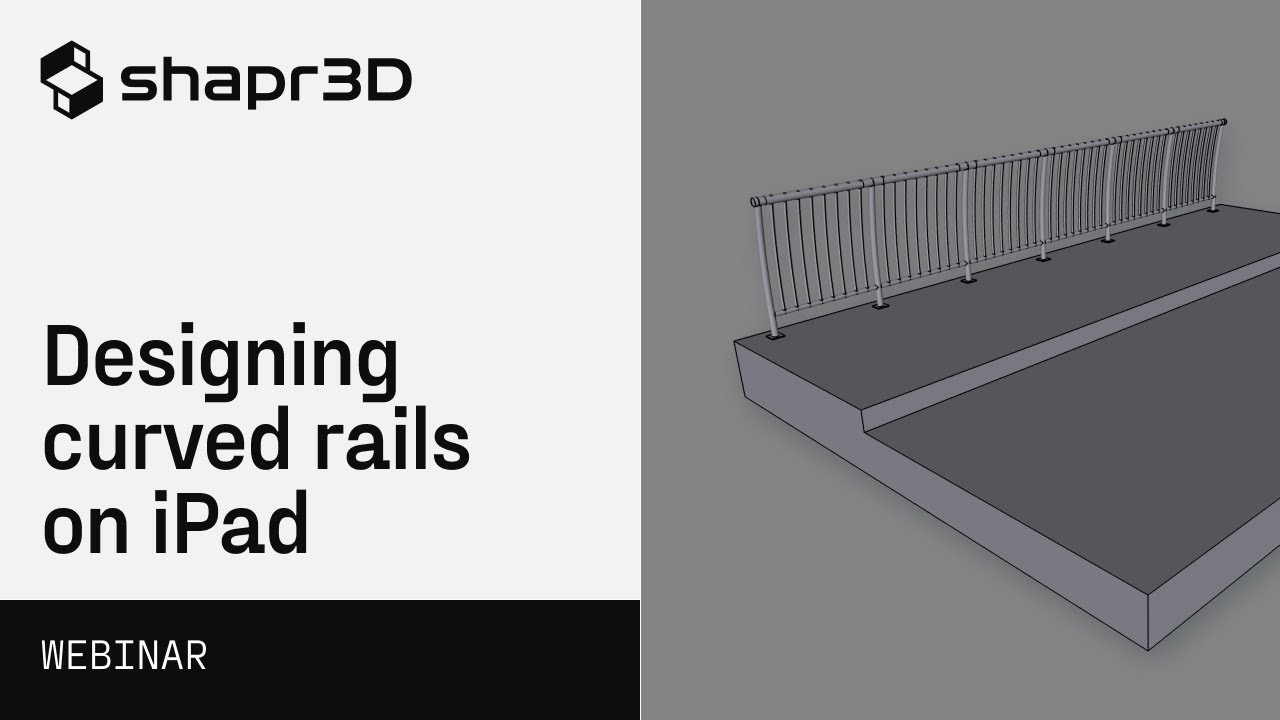
Let’s get started by visualizing our design on an empty canvas. Begin by creating a basic sketch that represents the street. Set your scene to inches, and extrude the street to your desired dimensions. This will serve as the foundation on which we will position our sketches and rail system.
Next, plan out the placement of your rail system. Start by drawing a horizontal pipe with a diameter of 75 inches. Ensure that the distance between the ring and the horizontal surface of the street is six inches. Use vertical lines and constraints to specify the desired distances accurately. Connect the rings with an arc that is tangent to the vertical lines for optimal positioning.
To connect the horizontal ring to the ground, draw two circles representing the pipe at the bottom, with diameters of 0.5 inches and 1 inch respectively. Position these circles in alignment and maintain a six-inch distance from the ground. This will create a seamless connection between the horizontal ring and the street.
Building the Concept Model
Now that we have planned out the design, it’s time to bring our concept to life. Start by extruding the various elements to their desired lengths. Use the copy function to replicate elements accurately and efficiently. By working in clean units, you can ensure that all elements align perfectly.
Continue by dividing the rail system into smaller segments. Determine the number of elements you want between each segment, and calculate the distance accordingly. Use the copy function to replicate these segments, ensuring consistent spacing throughout the rail system.
With the basic structure in place, it’s time to add strength and stability to our design. Use the shelling tool to hollow out the components, making them lightweight yet durable. This step is essential, as it allows us to create an efficient and aesthetically pleasing model.
Finalizing the Design
To complete the rail system, we need to create the connection and end parts. Start by creating a steel base that will be mounted onto the concrete. By adding a steel base, we can ensure a secure and stable rail system. Use the subtract function to create openings for the tubes and connectors, ensuring a seamless fit.
Next, create the connection parts using sketches and solid modeling tools. Carefully position and align the parts, ensuring a snug fit for easy assembly. Use the revolve function to create symmetrical shapes, and cut out unnecessary material to maintain a sleek and streamlined design.
Putting it All Together
Once all the individual parts are designed, it’s time to assemble the rail system. Weld or screw the metal parts together, ensuring a strong and sturdy structure. By following a precise sequence and attention to detail, you can ensure a seamless and efficient assembly process.
FAQs
-
What materials are used to build curved rails?
Curved rails are typically made from steel or aluminum, as these materials offer excellent strength, durability, and corrosion resistance. -
Can curved rails be customized to fit specific design requirements?
Yes, curved rails can be tailored to match any architectural design. The flexibility of the design process allows for customization and adaptation to suit specific project needs. -
Are curved rails suitable for outdoor applications?
Absolutely! Curved rails are well-suited for outdoor use, as they can withstand various weather conditions while maintaining their structural integrity.
Conclusion
Designing curved rails requires a combination of planning, sketching, solid modeling, and careful assembly. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can create a visually appealing and functional rail system for your architectural projects. Enjoy the process of bringing your designs to life and exploring the possibilities of curved rails.
For more insightful articles on technology and engineering, visit Techal.


