Revolutionize the way you control motor speed with Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs)
Do you ever wonder how electric motors operate at different speeds, tailored to specific requirements? It’s all thanks to Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs). In this article, we will delve into the world of VFDs, exploring their functionality and applications. So, fasten your seatbelts and get ready for an exciting journey into the realm of motor control.
Contents
Understanding the Basics
Electric motors, particularly alternating current (AC) motors, operate at a speed determined by the frequency of the power supply. The higher the frequency, the faster the motor’s rotation speed. In the United States, the standard AC power supply frequency is 60 Hertz, which results in a nominal rotation speed of 3600 RPM for a two-pole motor.
However, many applications do not require motors to operate at their full speed. This is where VFDs come into play. VFDs provide a flexible and precise solution to control motor speed by adjusting the frequency and voltage of the power supply. With their ability to generate ramps, frequencies, and voltages according to load requirements, VFDs ensure motors operate at desired speeds efficiently.
The Working Principles of VFDs
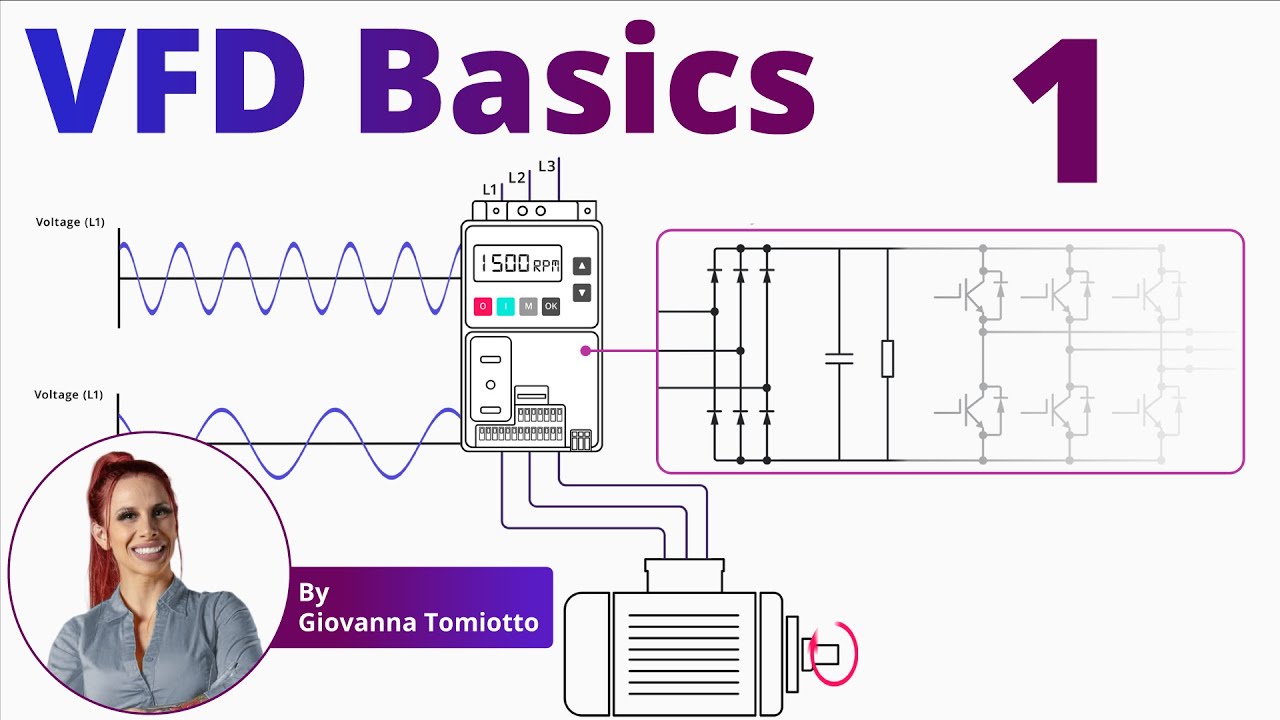
Now, let’s take a closer look at how VFDs work. A VFD consists of three main stages: the converter, the DC link, and the IGBT module.
The Converter: Transforming AC to DC
The converter, also known as a rectifier, is the first stage of a VFD. It converts the three-phase AC power supply into direct current (DC) using diodes arranged strategically in a six-pulse configuration. Analogous to check valves in a hydraulic system, these diodes only allow current flow in one direction. As each diode opens and closes, six pulses of current are generated, resulting in a waveform that resembles a series of pulses.
The DC Link: Filtering and Buffering
Following the converter, the DC link serves as a buffer, consisting of capacitors and resistors. It filters and smoothens the pulsed DC output from the converter, ensuring a stable power supply for the subsequent stage. The capacitors and resistors work together to maintain a uniform voltage across all capacitors in the link.
The IGBT Module: Converting DC back to AC
The final stage of the VFD is the IGBT (Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor) module. It converts the DC power back into AC, allowing for precise control of motor speed. This process, achieved through Pulse Width Modulation (PWM), regulates the width and frequency of the pulses that recreate the AC waveform. Part 2 of this article will provide a more in-depth understanding of the IGBT module and how PWM enables accurate control of motor speed.
Applications of VFDs
The versatility of VFDs makes them indispensable in numerous industrial and commercial applications. In the industrial sector, VFDs are employed in a wide range of machinery, from extruders and electric cranes to roller coasters and mechanical bulls. They offer unparalleled control and efficiency in these applications.
Commercially, VFDs find extensive use in pumps to regulate flow and volume in tanks. Additionally, they are widely adopted in the HVAC industry as a green technology, optimizing energy consumption in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems.
FAQs
-
Q: Why are VFDs important in motor control?
-
A: VFDs provide precise control over motor speed by adjusting the frequency and voltage of the power supply.
-
Q: What are the main components of a VFD?
-
A: A VFD consists of a converter (rectifier), a DC link, and an IGBT module.
-
Q: What are the applications of VFDs?
-
A: VFDs are used in various industrial and commercial applications, including machinery control, pump regulation, and HVAC systems.
For more frequently asked questions about VFDs and in-depth explanations, visit the Techal website.
Conclusion
Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs) revolutionize the way we control motor speed. By precisely adjusting the frequency and voltage of the power supply, VFDs ensure motors operate efficiently according to desired requirements. In this article, we explored the working principles of VFDs, from the conversion of AC to DC to the precise AC output using PWM. Stay tuned for Part 2, where we will delve deeper into the IGBT module and its role in motor control.
To discover more about the fascinating world of technology, visit Techal.


