Are you curious about encoders and how they are used in various industries? In this article, we will explore the fascinating world of encoders, their functions, and their wide range of applications. Whether you are a technology enthusiast or an engineer, this guide will provide you with insightful information about these devices.
Contents
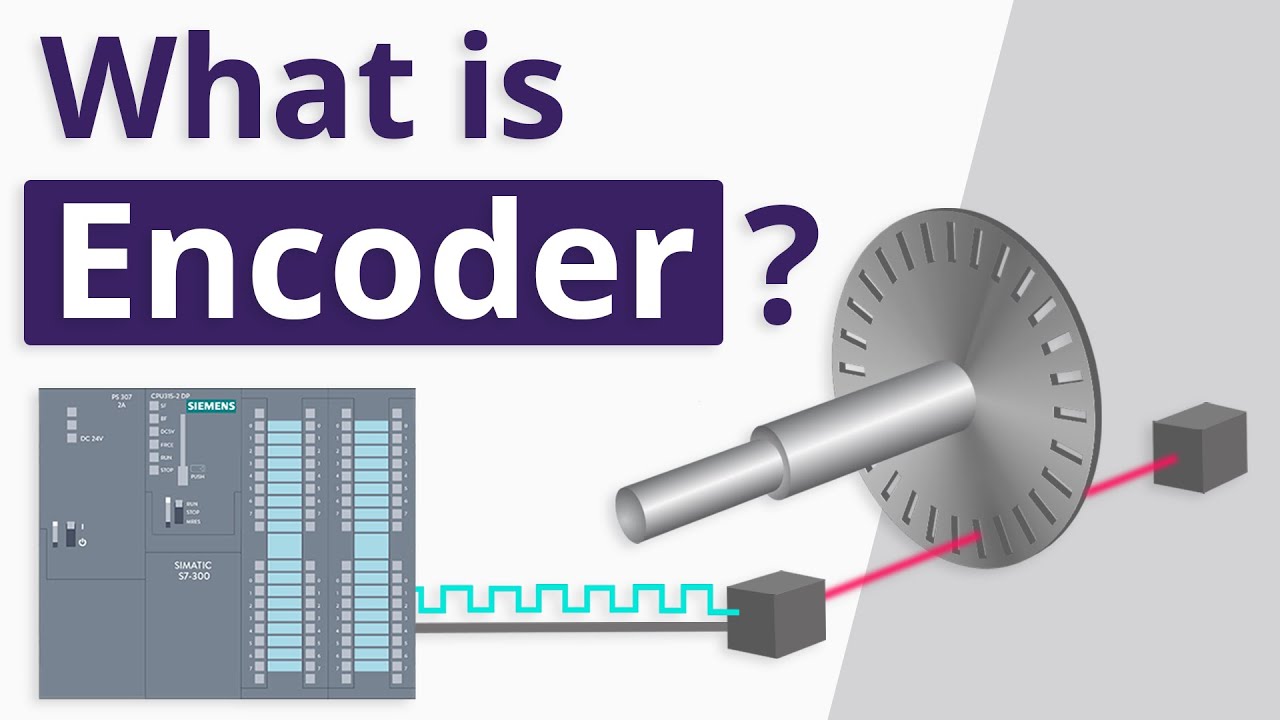
What Exactly is an Encoder?
At its core, an encoder is a device that provides feedback in many industries. Its main purpose is to sense position, direction, speed, or counts, regardless of the type. Encoders utilize motion and translate it into an electrical signal, which is then sent to a controlling device for interpretation and further use within a program.
Types of Encoder Technology
There are several technologies involved in encoders, including magnetic, mechanical, resistive, and optical. Out of these, optical encoders are the most widely used motion translating technology. They consist of opaque lines on a disk that a beam of light passes through. On the other side of the disk, a photo sensing device interprets the light based on the pattern on the disk.
Absolute vs. Incremental Encoders
Encoders can be classified into two main types: absolute and incremental. Absolute encoders provide a unique digital code for each position, allowing the exact position to be determined immediately. On the other hand, incremental encoders provide relative position information by tracking changes in position over time.
Applications of Encoders
Encoders have a wide range of uses in various industries. Some examples include:
Closed-Loop Applications: Servo or VFD Control
In applications involving pump control, encoders are used to provide feedback on speed. For example, when filling a tank with a liquid, an encoder attached to the VFD (Variable Frequency Drive) can verify that the pump is operating at the requested speed.
Measuring Processes
In processes that require precise measurements, encoders play a crucial role. For instance, when cutting aluminum sheets to specific sizes, an encoder attached to a conveyor can indicate the length of material that has been fed, helping adjust the cutting blade accordingly.
Counting Applications
Encoders are also used for counting purposes. In a scenario where bottles move on a conveyor line, encoders can count the number of bottles that enter and exit an assembly, ensuring that the same number of bottles exits within a predetermined time frame.
Conclusion
Encoders are essential devices that provide valuable feedback in various industries. Whether it’s controlling pumps, measuring materials, or counting objects, encoders play a vital role in ensuring accuracy and efficiency. By understanding their functions and applications, you can harness the power of encoders to optimize processes in your field.
FAQs
Q: What is the difference between absolute and incremental encoders?
A: Absolute encoders provide a unique code for each position, while incremental encoders track changes in position over time.
Q: What are the different technologies used in encoders?
A: Encoders can utilize magnetic, mechanical, resistive, or optical technologies.
Q: What are some common applications of encoders?
A: Encoders are used in closed-loop applications for servo or VFD control, measuring processes, and counting applications.
For more detailed information on encoders and other technology topics, visit Techal.
Note: The content of this article is a unique, rewritten version of the original text provided.


