In the world of industrial automation, two terms often cause confusion: SCADA and HMI. While they share some similarities, they are actually different components of a larger system. Let’s explore the distinctions between SCADA and HMI, their functionalities, and how they are used in various industries.
Contents
SCADA: Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition
SCADA, which stands for “Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition,” is a comprehensive system used for monitoring and controlling large areas, such as entire sites or plants. It is a combination of multiple systems, including sensors, RTUs (Remote Terminal Units), and PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers). These systems collect and transmit data to the central SCADA unit.
The SCADA unit, equipped with its own HMI (Human Machine Interface), can monitor and control anything connected to it. It acts as the control center, gathering data from various sources and providing a user-friendly interface for operators to monitor and manage operations efficiently.
HMI: Human Machine Interface
On the other hand, an HMI, which stands for “Human Machine Interface,” is an interface used by humans to interact with a machine or process. It is typically a touchscreen or a screen with buttons attached, allowing operators to monitor and control specific functions of the machine. In most cases, an HMI is connected to a compatible PLC, enabling seamless communication and functionality.
Now, let’s dive deeper into a real-world scenario to better understand how SCADA and HMI work together.
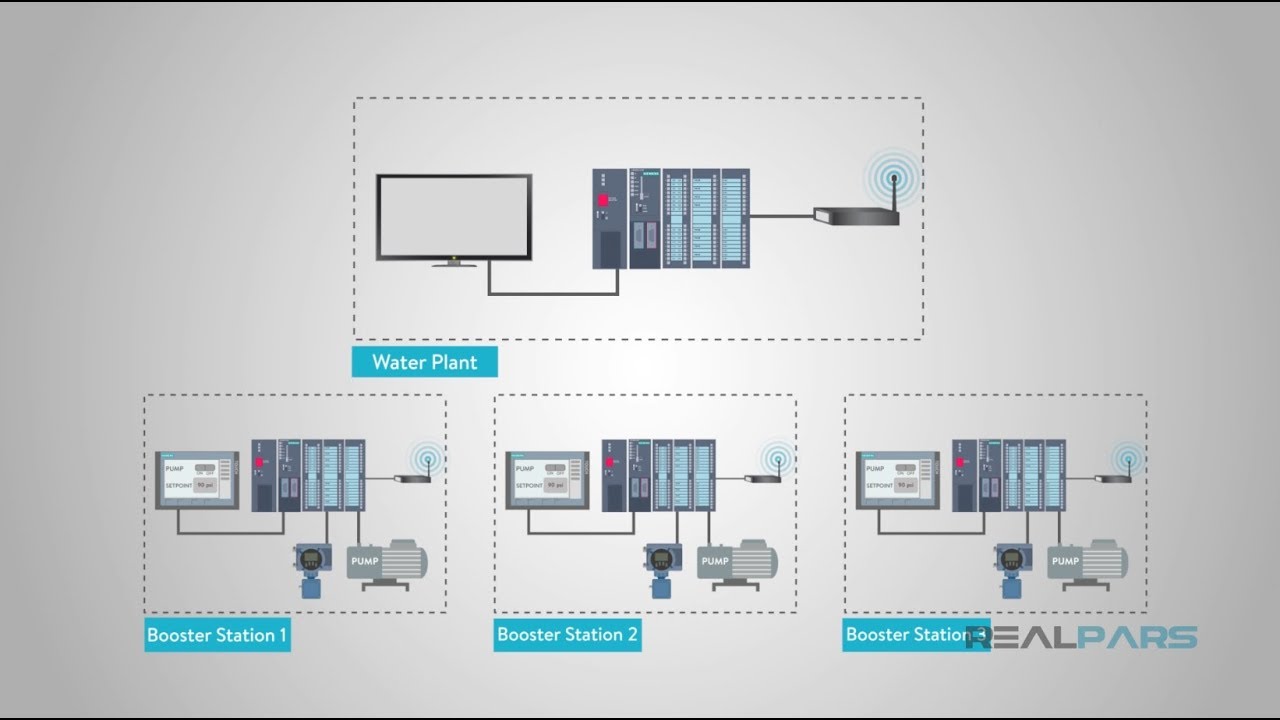
SCADA and HMI in Action: Water Treatment Facility
Imagine working in a water and wastewater treatment facility. Here, a SCADA system and HMI play a crucial role in ensuring efficient operations. The main water plant houses the HMI, which is connected to the central SCADA unit.
The SCADA system displays each booster pump station within the water district on the screen. At each location, a PLC is connected to sensors that monitor water flow, pressure, and other parameters. The PLC controls and operates the pump itself. The remote SCADA unit, connected to the PLC system, enables operators at the main plant to control and monitor every pump station effectively.
The advantages of a well-implemented SCADA system are notable. It saves companies significant time and labor, streamlines operations, and enhances productivity.
To simplify the concept, let’s use a car analogy. Just as a modern vehicle has multiple sensors connected to different computers, a SCADA system comprises various remote systems linked to a central hub. The HMI, similar to the main screen in a car’s dash, allows operators to monitor and control operations through user controls.
In summary, SCADA and HMI are distinct components that work together to create a powerful industrial tool. SCADA systems enable efficient monitoring and control of multiple systems, while HMIs provide a user-friendly interface for operators to interact with specific machines or processes.
If you want to delve deeper into the world of HMIs, be sure to check out the RealPars video series on the topic.
Remember that Techal is your go-to destination for all things technology! Check out their website Techal for more insightful articles and resources.
Now, armed with a clear understanding of SCADA and HMI, you’re ready to excel in the world of automation and controls engineering. Head over to realpars.com to discover a wealth of training materials and videos to advance your knowledge in PLC programming and secure high-paying job opportunities in this sought-after field. Don’t miss out on this incredible opportunity!


