In the realm of technology, remote control and monitoring systems play a crucial role in managing field devices and ensuring seamless operations. One such system, known as the Remote Terminal Unit (RTU), has gained significant importance in recent years. In this article, we will explore the world of RTUs, their advantages, and their place alongside Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) in the ever-evolving landscape of industrial automation.

Contents
What is an RTU?
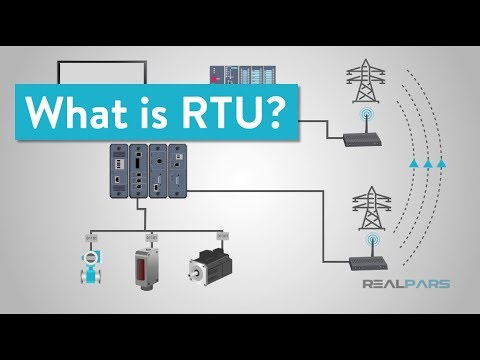
RTU stands for Remote Terminal Unit, also referred to as Remote Telemetry Unit or Remote Telecontrol Unit. These microprocessor-based devices serve as the bridge between field devices and plant control or SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems. Primarily, the RTU is responsible for monitoring and controlling various field devices, gathering data, and transmitting it to centralized control systems for analysis and decision-making.
Comparing RTU and PLC
While some may claim that RTUs are more powerful than PLCs due to their ability to support multiple inputs and outputs, it is important to note that PLCs offer similar capabilities. However, where the RTU shines is in its ruggedness and ability to operate in harsh environments. With superior environmental tolerances, backup power options, and autonomy, RTUs are often the preferred choice for remote and challenging locations.
Programming Flexibility
RTUs offer a unique advantage in terms of programming flexibility. While PLCs require specialized software and skills in ladder logic, structured text, and function block programming, some RTUs provide a simpler alternative. They can be programmed through a user-friendly web interface or setup software, eliminating the need for extensive training. Additionally, many RTUs come with preprogrammed modules that can be easily applied to specific functions.
Environmental Tolerances
One of the standout features of RTUs is their ability to withstand extreme temperatures and operate in remote locations. These units are frequently used in off-shore oil rigs, mountainous areas, and other challenging environments. To ensure reliable communication, RTUs often utilize radio, microwave, and satellite technologies, enabling seamless data transmission even in the most remote locations.
Furthermore, some RTUs are equipped with backup power options, such as solar panels or batteries, ensuring continuous operation in the event of a power outage. While PLCs can also have UPS backup, the charging circuit in RTUs provides an added advantage.
The Rise of PLCs and PACs
In recent years, Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) and Programmable Automation Controllers (PACs) have emerged as strong competitors to RTUs. These advanced systems offer similar advantages, making the choice between them more challenging. With advancements in technology, PLCs and PACs are now capable of matching the environmental tolerances and programming flexibility provided by RTUs.
Conclusion
As the world of industrial automation continues to evolve, RTUs remain a powerful tool for remote control and monitoring. Their ruggedness, environmental tolerances, and programming flexibility make them a preferred choice in challenging conditions. However, PLCs and PACs have caught up, offering similar capabilities and bridging the gap between these once distinct systems. To stay at the forefront of technology, it is crucial to explore the options available and discover which solution best suits your unique requirements.
FAQs
Q: What does RTU stand for?
A: RTU stands for Remote Terminal Unit, which is a microprocessor-based device used for remote control and monitoring of field devices.
Q: How does an RTU differ from a PLC?
A: While both RTUs and PLCs offer similar capabilities in terms of inputs, outputs, and process control, RTUs excel in ruggedness, environmental tolerances, and remote operation in challenging locations.
Q: Can RTUs be programmed easily?
A: Some RTUs provide a user-friendly web interface or setup software for programming, eliminating the need for extensive programming skills. However, others may require specialized languages such as ladder logic or structured text.
Q: Are RTUs still relevant in today’s technology landscape?
A: Despite the rise of PLCs and PACs, RTUs remain relevant due to their superior environmental tolerances and suitability for remote and challenging locations.
Conclusion
In the realm of industrial automation, Remote Terminal Units (RTUs) continue to play a vital role in remote control and monitoring systems. These rugged devices offer superior environmental tolerances and programming flexibility, making them ideal for challenging locations. However, with the advancements in PLC and PAC technology, the gap between these systems is closing. To stay ahead in the ever-evolving technology landscape, it is crucial to explore the options and determine the best solution for your specific needs.
For more information and training materials on PLC programming, visit Techal. Stay tuned for more insightful analysis, comprehensive guides, and the latest tech facts from Techal!