In the previous section, we discussed the importance of data visualization and the need to effectively communicate data visually. We emphasized the need to know your audience and the story you want to convey, while avoiding any misleading representations of the data. In this section, we will continue the discussion on data visualization but focus specifically on the use of color maps.
Back in the 80s, when software options were limited, visualizing data required manual graph plotting. Today, with the advent of computers, creating graphs and figures has become much easier. However, it has also introduced some pitfalls that we need to be aware of. One of the most common mistakes in creating scientific figures lies in the misuse of color maps.
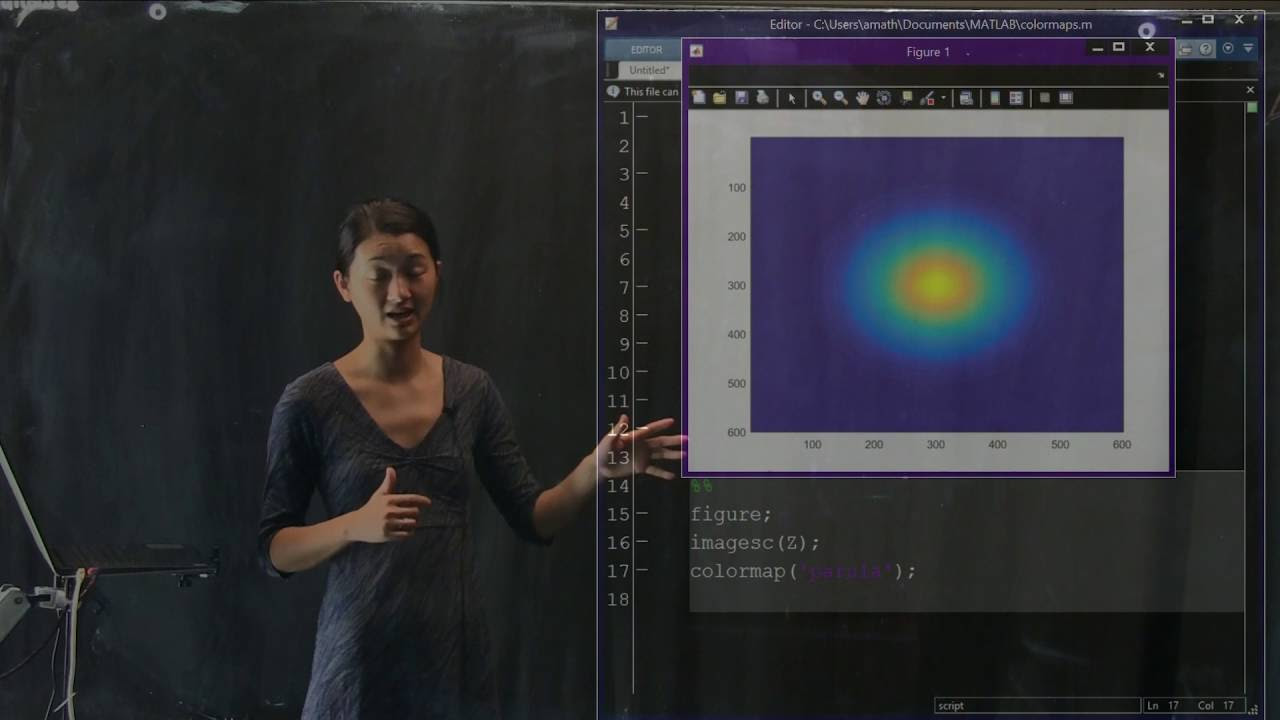
To illustrate this, let’s create a simple example using a Gaussian distribution. We will plot a one-dimensional data set as a two-dimensional graph. By rotating this “traffic cone” shape, we can visualize it in 3D. However, instead of relying on 3D plots, which can obscure data, it is often more effective to represent the data as an image.
To convert the data into an image, we can use the image or imageSC command. By doing so, we can avoid the issues of contour plots where information is hidden. The image representation provides a clear view of the data without any obstructions.
Now, let’s explore the different color maps that can be used to represent the data. One commonly used color map is “jet.” Although it offers high contrast, it can create misleading features, such as ridges and rings that don’t actually exist in the data.
To address this issue, an alternative is to use a grayscale color map. While this eliminates the problem of emphasizing certain regions, it lacks contrast and may make it difficult to distinguish small differences between neighboring values.
A more balanced option is the “parula” color map, which is now the default in MATLAB. It offers a good compromise between visual interest, contrast, and accuracy. It provides clear distinctions between different regions of the data without introducing misleading features.
Another color map to consider is “HSV.” However, this color map can be highly misleading, as it uses circular mapping. It assigns the same color to both the highest and lowest values, making it difficult to differentiate between peaks and valleys.
If none of the built-in color maps suit your needs, you can create your own custom color map using RGB values. This allows you to tailor the colors to your specific requirements. However, be cautious not to introduce artificial features or misrepresent the data.
In conclusion, choosing the right color map is essential in effectively communicating data. It is important to consider the purpose of the visualization and the story you want to tell. Understanding the potential pitfalls and limitations of different color maps will help ensure that your representation accurately conveys the intended message.
To learn more about data visualization and other technology topics, visit Techal.org.
Contents
FAQs
Q: What is a color map?
A: A color map is a matrix of RGB values used to assign colors to different regions of a visualization based on data values. It helps convey information and add visual interest to graphs and figures.
Q: Can I create my own color map?
A: Yes, you can create your own custom color map by specifying RGB values for different colors. This allows you to tailor the colors to your specific needs and preferences.
Q: What should I consider when choosing a color map?
A: When choosing a color map, consider the purpose of the visualization, the story you want to tell, and the potential pitfalls of using different color maps. Strive for accuracy, clarity, and effective communication of the data.
Q: How can I avoid misleading representations of data?
A: To avoid misleading representations of data, be cautious of color maps that introduce artificial features or emphasize certain regions unfairly. Choose color maps that accurately represent the data without distorting its true nature.
Conclusion
The use of color maps in data visualization plays a crucial role in effectively communicating information. It is important to understand the limitations and potential pitfalls of different color maps to ensure accurate representation of the data. By choosing the right color map and considering the purpose of the visualization, you can tell a compelling data story that engages and informs your audience.
Visit Techal.org for more informative articles on technology-related topics.


