If you’ve ever worked in automated systems and manufacturing industries, you would know that PID control is considered the gold standard for process control applications. PID control, which stands for Proportional-Integral-Derivative control, is widely used in industrial control loops to ensure precise control of processes. In this article, we will explore PID control and compare it to two advanced techniques: Fuzzy Logic Control and Model Predictive Control.
Contents
The Basics of PID Control
PID control consists of three main components: Proportional, Integral, and Derivative. The Proportional component applies an effort based on how far the process is away from the setpoint. The Integral component helps bring the process back to the setpoint by applying an effort over time. The Derivative component assesses the speed at which the process is moving away from the setpoint and adjusts the controller output accordingly.
PID control is popular for several reasons. Firstly, it has been around for a long time and is taught to engineers and technicians in every college and university. Additionally, Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) and Distributed Control Systems (DCSs) have built-in PID functionality, making it easily accessible for implementation. PID control is simple, versatile, and reliable, making it suitable for many applications.
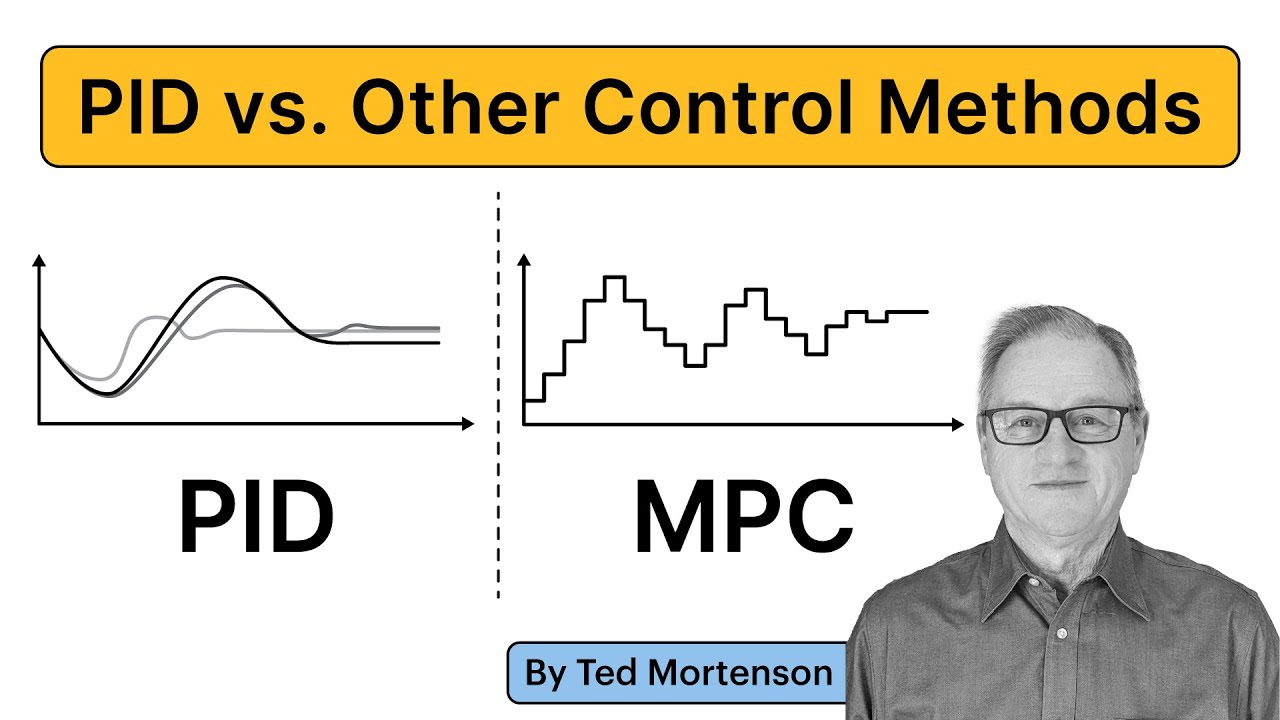
However, PID control may not always be the best choice for every scenario. For example, in motion control systems where precise speed and position are critical, a quarter-wave response produced by PID control may not be acceptable. In such cases, more advanced control techniques like Fuzzy Logic Control and Model Predictive Control come into play.
Fuzzy Logic Control (FLC)
Fuzzy Logic Control (FLC) is a feedback control algorithm that expands on the binary logic concept. While binary logic has only two possibilities (True or False), FLC allows for multiple possibilities. It introduces linguistic variables and membership functions to describe the degree of membership of input or output variables.
For example, FLC can assign temperature values between “Hot” and “Cold” rather than just “True” or “False.” Fuzzy sets and membership functions help quantify the fuzzy logic involved in decision-making processes. FLC utilizes IF-THEN rules based on linguistic terms to relate input variables to the output variable. The process involves fuzzification, fuzzy inference, and defuzzification to convert input values into real-world output values.
Model Predictive Control (MPC)
Model Predictive Control (MPC) is a feedback control technique that uses a mathematical model to predict the behavior of the process variable. Unlike PID control, which adjusts the control output based on input data, MPC predicts the future behavior of the system based on the model and optimizes control actions accordingly.
MPC is particularly effective in systems with multiple interacting variables, such as industrial processes, robotics, and autonomous vehicles. It utilizes the robot model’s kinematics and dynamics, along with an optimization algorithm, to calculate the optimal control inputs over a predetermined period. The calculated control input trajectory is then applied to the system to achieve the desired behavior.
Conclusion
PID control remains the go-to choice for many simple process control applications. Its simplicity and widespread implementation make it accessible and reliable. However, for more complex systems with specific requirements, advanced control techniques like Fuzzy Logic Control and Model Predictive Control offer unique advantages.
Understanding the strengths and suitability of each control method is crucial for selecting the right approach for your application. While PID control is a solid foundation, exploring other alternatives like Adaptive Control and Neural Network Control can open up even more possibilities for precise and efficient control.
For more in-depth information on PID control, consider signing up for the “PID Controller Basics” course offered by RealPars. Empower yourself with knowledge and stay ahead in the ever-evolving world of technology.
FAQs
1. What is PID control?
PID control stands for Proportional-Integral-Derivative control and is a widely used feedback control algorithm in industrial processes. It consists of three main components that work together to ensure the controlled process closely follows the setpoint.
2. What are the advantages of PID control?
PID control is popular due to its simplicity, versatility, and reliability. It has been widely taught and implemented in various systems, and many PLCs and DCSs have built-in PID functionality. PID control provides an acceptable response for many process control applications.
3. When should I consider using Fuzzy Logic Control?
Fuzzy Logic Control (FLC) is suitable for systems where linguistic variables and human input are involved. It allows for more than just binary possibilities and can handle complex decision-making processes based on linguistic terms. FLC is often used in consumer appliances and systems with non-linear characteristics.
4. Is Model Predictive Control suitable for my application?
Model Predictive Control (MPC) works well in systems with multiple interacting variables and complex dynamics. It utilizes a mathematical model to predict the future behavior of the system and optimize control actions accordingly. MPC finds applications in industrial processes, robotics, and autonomous vehicles.
5. Are there other alternatives to PID control?
Yes, apart from Fuzzy Logic Control and Model Predictive Control, there are other alternatives such as Adaptive Control and Neural Network Control. These advanced control techniques offer unique advantages and are suited for specific applications.
Conclusion
PID control stands as the gold standard for many process control applications. However, when faced with complex dynamics and specific requirements, alternative control methods like Fuzzy Logic Control and Model Predictive Control prove to be valuable. Understanding each technique’s strengths and suitability empowers engineers and technicians to make informed decisions when choosing the right control approach for their applications. Stay curious and keep exploring the ever-evolving world of control systems.
Click here to learn more about the Techal brand and stay up to date with the latest technological advancements.

