Welcome to the world of motion control! In this article, we will delve into the fascinating realm of Linear Motion Control. Whether you are an engineering enthusiast or a professional in the field, this article will provide you with valuable insights into the applications and mechanisms of linear motion control.
Contents
Understanding Linear Motion Control
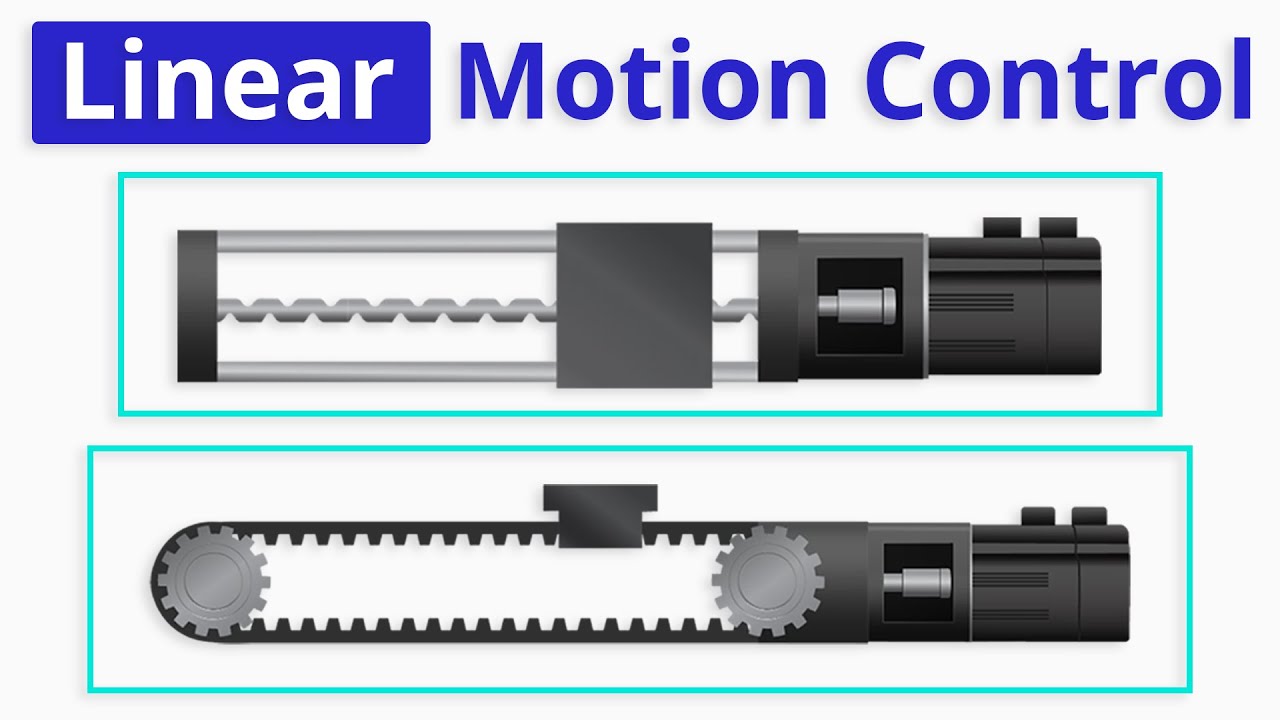
Linear motion control involves various technologies such as linear motors, linear actuators, and linear rolling guides and bearings. These systems play a crucial role in industrial automation, machinery, computer peripherals, packaging, medical imaging, robotics, and many other applications.
Linear drives are employed to move carriages to desired positions, and the most commonly used drive technologies include ball-screw drives, lead-screw drives, and belt drives. The configuration of a linear motion control system, including the number of axes of motion, is an important consideration.
Factors to Consider in Linear Motion Control
When selecting a linear motion control system, several factors need to be taken into account. Here are some key considerations:
System Orientation and Mounting
The orientation and mounting of the system play a vital role, especially in multi-axis systems. Factors to consider include the direction of travel for each axis, whether the load needs to move simultaneously in multiple axes, and the positioning of the actuators at different angles to the horizontal.
Force, Speed, and Travel Distance
Determining the required force involves considering the weight and friction of the object being lifted or moved. Speed is another crucial factor, as it determines the mechanical power required. The travel distance, known as the stroke length, is also an important consideration when choosing a suitable linear motion control drive system.
Accuracy, Repeatability, and Lifetime Requirements
Accurate and repeatable motion is often crucial in many applications. Factors such as the desired precision, repeatability, and duty cycle need to be taken into account. Duty cycle refers to how often the actuator will operate and the time elapsed between movements. Additionally, the lifetime requirement and the expected number of repetitions per unit of time should be considered.
Actuator Options
There are various linear actuators to choose from, such as lead-screw actuators, ball screw actuators, and planetary roller actuators. Lead-screw actuators are cost-effective and widely used, while ball-screw actuators offer less friction and higher thrust capacity. Planetary roller screw actuators are the most durable but also the most expensive option. Belt-driven linear positioning tables are suitable for high-speed and long-travel applications.
Linear Motion Control Applications
Linear motion control finds applications in a wide range of industries. Some examples include:
- Industrial machines: Linear motion control is used for positioning loads, palletizing, packaging, pick-and-place operations, filling operations, and automated warehouses.
- Medical applications: Linear motion control is vital in operating room beds, X-ray machines, MRI and CT scanners, dentist chairs, and medical diagnostics and treatment equipment.
- Lab automation: Linear motion control is used for pick and place operations, DNA sampling, cell culture, drug testing, and drug dispensing in medical labs.
- Assembly lines: Linear motion control plays a crucial role in positioning materials, assembly tools, and equipment along assembly lines.
- Food industry: The food industry relies on fast and accurate material handling equipment to keep up with high-speed production lines.
These are just a few examples of the numerous applications where linear motion control is indispensable.
FAQs
Q: What is linear motion control?
A: Linear motion control involves various technologies such as linear motors, linear actuators, and linear rolling guides and bearings. It is used in industrial automation, machinery, computer peripherals, packaging, medical imaging, robotics, and other applications.
Q: What factors should be considered when selecting a linear motion control system?
A: When selecting a linear motion control system, factors such as system orientation and mounting, force, speed, travel distance, accuracy, repeatability, lifetime requirements, and actuator options need to be taken into account.
Q: Where is linear motion control used?
A: Linear motion control finds applications in various industries, including industrial machines, the medical field, lab automation, assembly lines, and the food industry.
Conclusion
Linear motion control is a fascinating field that enables precise and accurate movements in various industrial applications. Understanding the mechanisms and factors involved in linear motion control is essential for designing and implementing successful motion control projects. If you want to learn more about linear motion control and other related topics, visit Techal for insightful articles and comprehensive guides.
Click here to visit Techal for more technology insights.