Welcome to the world of subnetting! In this guide, we will lay the foundation and answer the core question: what is subnetting? Whether you’re a technology enthusiast or an engineer, understanding subnetting is essential. So let’s dive in and uncover the intricacies of this concept that forms the backbone of networking.
Contents
What is Subnetting?
At its core, subnetting involves taking one network and dividing it into smaller subnetworks. For example, let’s consider the IP address range 10.0.0.0 to 10.0.0.255. This range contains 256 IP addresses and is referred to as a slash 24 network. But subnetting allows us to break this network into smaller parts, like slash 25, slash 27, slash 26, and so on.
Seven Essential Subnetting Attributes
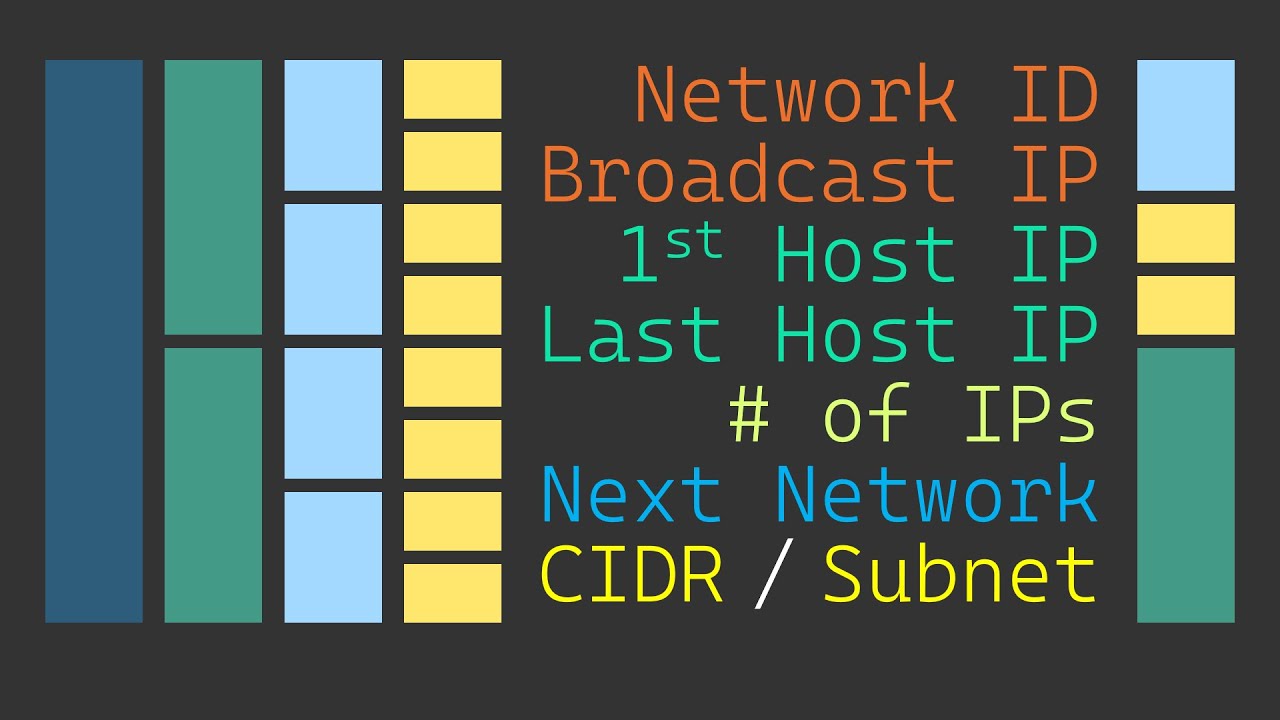
When subnetting, there are seven key pieces of information you need to extract from each subnet. These attributes are essential for solving any subnetting problem you may encounter. Let’s explore each attribute:
-
Number of IP Addresses: This refers to the total count of addresses in each subnet. For instance, a slash 24 network has 256 addresses, while a slash 27 has 32 addresses.
-
Subnet Size: Subnets are often referred to using cider notation (e.g., slash 25) or subnet mask notation (e.g., 255.255.255.0). Both notations indicate the size of a subnet or the number of IP addresses it contains.
-
Network ID: The network ID is the first possible address in each subnet. It serves the purpose of identifying a specific subnet. For a slash 25 subnet, the network ID would be 10.0.0.0.
-
Broadcast IP: The broadcast IP is the last possible address in each subnet. It allows the user to communicate with every other IP address within the subnet. For a slash 25 subnet, the broadcast IP would be 10.0.0.127.
-
Usable IP Range: To determine the usable IP range, you need to find the first host IP and the last host IP. The first host IP immediately follows the network ID, while the last host IP is just before the broadcast IP.
-
Next Network: The next network is simply the network ID of the subnet that follows. It can be calculated by adding 1 to the broadcast IP of the current subnet.
Now that we understand the seven attributes, let’s take a closer look at how to solve for each one.
Solving for Subnetting Attributes
To simplify subnetting calculations, we will be using a cheat sheet. This cheat sheet can help you determine each attribute more efficiently. In the next video, we will show you how to draw the cheat sheet, and subsequently, how to use it effectively.
With the cheat sheet and the instructions provided in this video series, you will be able to solve for all seven attributes in 60 seconds or less. Mastery of subnetting is within your reach!
FAQs
Q: How can subnetting benefit network architecture?
A: Subnetting allows for efficient allocation of IP addresses and enhanced network security. By dividing a large network into smaller subnets, network administrators can better manage resources and isolate potential security risks.
Q: Are there any limitations to subnetting?
A: While subnetting offers numerous advantages, it does require careful planning and management. Poorly designed subnets can result in inefficient network performance and increased complexity.
Q: Can I use online tools for subnetting calculations?
A: Yes, there are many online subnet calculators available that can assist you in subnetting calculations. However, understanding the underlying principles and calculations involved will enable you to develop a deeper understanding of subnetting overall.
Conclusion
Subnetting is a fundamental concept in networking that allows us to divide a network into smaller, more manageable parts. By mastering the seven subnetting attributes covered in this guide, you’ll be equipped to solve any subnetting problem that comes your way. Keep exploring the world of technology with Techal.
Visit Techal for more insightful articles and guides.
Image Source: Unsplash


