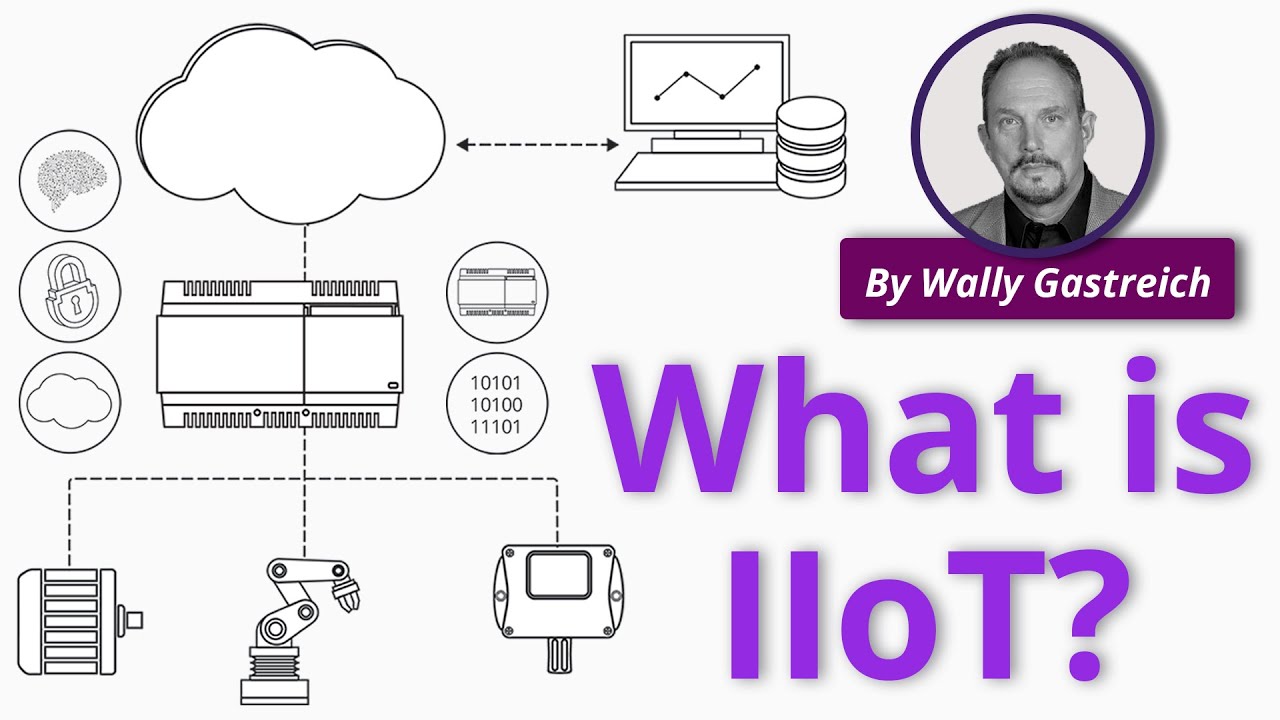
The world of technology is constantly evolving, and one of the most significant advancements in recent years is the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT). This revolutionary concept combines automation, cloud computing, and artificial intelligence to improve productivity and efficiency in various industries, including manufacturing, healthcare, and logistics. In this article, we will delve into the details of the IIoT and explore its importance in the age of Industry 4.0.
Contents
What is the Industrial Internet of Things?
While the IIoT falls under the broader category of the Internet of Things (IoT), there is a key difference between the two. While IoT focuses on consumer-based devices like Fitbits and smart home appliances, the IIoT centers around the connection of machines and devices in industrial sectors. By leveraging interconnected instruments, sensors, and other devices, the IIoT enables computer-driven industrial applications, revolutionizing manufacturing and energy management.
The Role of Digital Transformation
To fully understand the potential of the IIoT, we must also grasp the concept of digital transformation. Digital transformation involves digitizing a business and creating a unified data space, allowing for seamless communication between enterprise and control systems. The International Society of Automation’s standard, known as ISA 95, provides an automated interface model that facilitates this integration. However, communication between different applications within an organization can pose challenges, leading to inefficient data management. The IIoT aims to address these issues by providing real-time data, empowering stakeholders to make informed decisions without relying on outdated reports.
Key Technologies Driving the IIoT
The IIoT relies on several key technologies to achieve its objectives. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) play crucial roles in developing intelligent machines that can respond like humans and predict outcomes accurately. Cybersecurity ensures secure communication between disconnected machines in the IIoT network. Cloud computing allows for the use of IT services and facilitates the upload and download of files from internet-based servers. Edge computing optimizes the processing of data by bringing storage closer to where it is needed. Data mining and analytics consolidate and analyze large amounts of data from various parts of an enterprise, enabling valuable insights and informed decision-making.
Benefits and Risks of the IIoT
Implementing the IIoT can bring numerous benefits to organizations. Improved productivity, just-in-time manufacturing, and better inventory control contribute to increased competitiveness and customer satisfaction. Additionally, the concept of a digital twin, a virtual replica of physical assets and processes, allows for experimentation and learning in a safe environment. However, the adoption of the IIoT also comes with risks, including the high cost of data integration, lack of expertise, implementation difficulties, and potential cyber threats. Overcoming these challenges requires investment in new software, hardware, and training, as well as expertise in machine learning and real-time analytics.
FAQs
Q: What is the difference between IoT and IIoT?
A: While IoT focuses on consumer-based devices, IIoT centers around the connection of machines and devices in industrial sectors.
Q: What technologies drive the IIoT?
A: The IIoT relies on artificial intelligence, cybersecurity, cloud computing, edge computing, and data mining.
Q: What are the benefits of implementing the IIoT?
A: The IIoT offers improved productivity, better inventory control, increased competitiveness, and enhanced decision-making capabilities.
Q: What are the risks of adopting the IIoT?
A: Potential risks include the cost of data integration, lack of expertise, implementation difficulties, and cybersecurity threats.
Conclusion
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is revolutionizing industries by leveraging automation, cloud computing, and artificial intelligence. By connecting machines and devices, the IIoT enables real-time data analysis and informed decision-making, ultimately driving increased productivity and efficiency. While the implementation of the IIoT comes with challenges, organizations that embrace this transformation can gain a competitive edge in the era of Industry 4.0. To learn more about the IIoT and its applications, visit Techal.