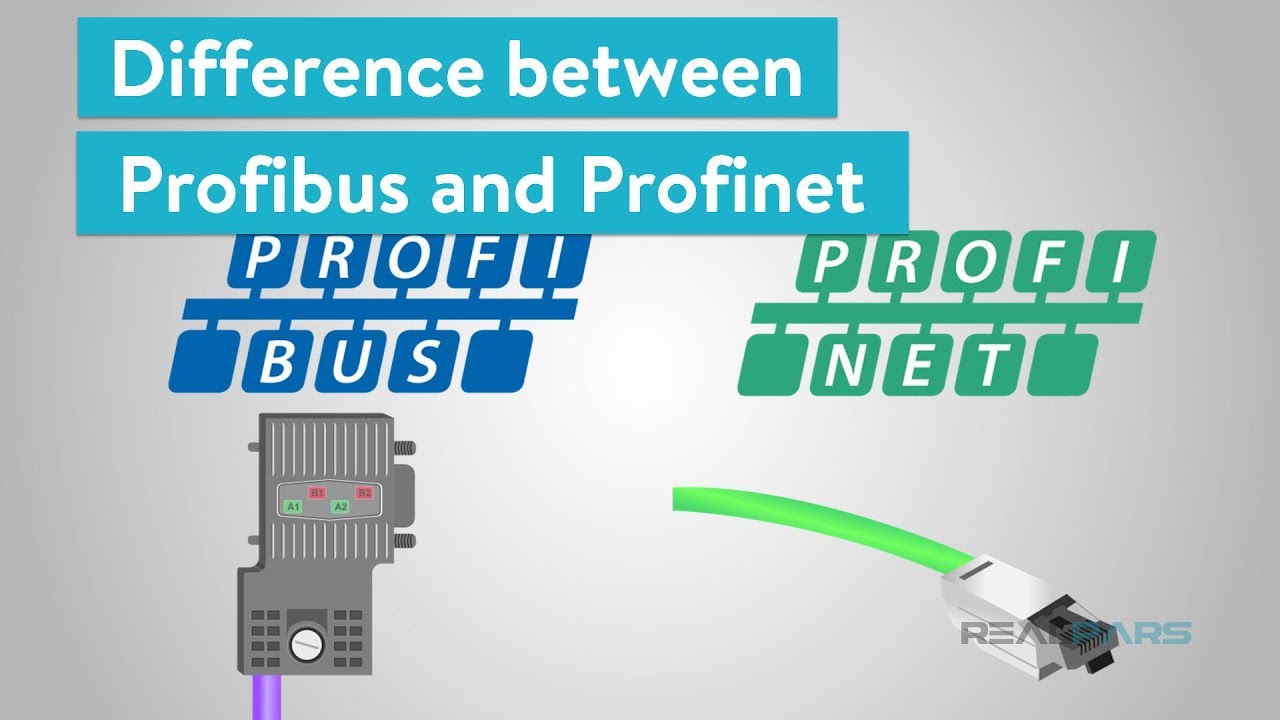
In the world of Siemens control systems, two communication protocols reign supreme: Profibus and Profinet. At first glance, they may seem quite similar, but don’t be fooled. These protocols have distinct differences that set them apart, from the cables and connectors they use to their underlying technologies. Let’s dive into the fascinating world of Profibus and Profinet and uncover their unique characteristics.
The Tried and True Profibus
First introduced in 1993, Profibus, short for “PROcess FIeld BUS,” is an established industrial communication protocol with a rich history. Over 50 million devices were installed by the end of 2017, making it a widely adopted technology in various control applications.
You may recognize a Profibus connection port as it resembles a standard DB-9 serial connector. However, appearances can be deceiving, as the underlying protocol is entirely different. Most Profibus cables feature a distinctive purple outer jacket, making them easily identifiable. Some connectors even have a pass-through port at the back, allowing for daisy-chaining of devices.
Important to note is the presence of a red switch on both types of connectors. This switch controls the Terminating Resistor, which signifies the end of the Profibus network. It must be set to the “on” position on the last device and “off” for all other devices. Incorrect switch settings can lead to bus faults and disruptions.
Each device on a Profibus network requires a unique address ranging from 1 to 127. Configuring the address depends on the device, with some using STEP7 or TIA Portal, while others utilize dip switches at the front. Profibus networks operate at speeds ranging from 9600 bits per second to 12 megabits per second, with cable length limitations for higher data rates.
The New Kid on the Block: Profinet
In contrast, Profinet represents a newer generation of industrial communication protocols, leveraging Ethernet technology. It employs a standard RJ-45 Ethernet jack as the physical interface, instantly recognizable by its strikingly green cables. While a standard Ethernet cable may suffice for connecting two Profinet devices in some cases, it is advisable to use official Profinet cables. These cables are designed with robust shielding to thrive in demanding industrial environments.
Profinet operates at a blazing speed of 100 megabits per second and supports cable lengths of up to 100 meters. Thanks to its remarkable response time of less than 1 millisecond, Profinet is the go-to choice for high-speed applications. Another advantage of Profinet is its compatibility with standard Ethernet switches, enabling effortless network expansion.
Unlike Profibus, Profinet devices possess three address types: IP address, MAC address, and device name. While IP and MAC addresses are common to all Ethernet devices, the device name is exclusive to Profinet devices. As an automation engineer, your focus will primarily revolve around configuring Device Names and IP addresses for your Profinet networks.
The Path to Industrial Success
With its higher speed and enhanced flexibility, Profinet is fast becoming the communication protocol of choice for industrial applications. However, Profibus still holds a significant presence in the field. As a controls engineer, it is vital to familiarize yourself with both protocols as they play crucial roles in your job.
If you’re eager to take your career to the next level and delve into the realm of PLC programming, visit Techal for easy-to-understand tutorials. Unleash your potential and master the world of industrial automation.

