Welcome to Techal! In this article, we will explore the intricacies of library normalization using the popular statistical method called edgeR. Developed by the genetics department at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, edgeR offers a unique approach to library normalization that addresses sequencing depth and library composition.
Contents
Understanding the Need for Library Normalization
Before diving into the details of edgeR, it’s important to understand why library normalization is essential in genomic analysis. Traditional normalization techniques like RPKM (Reads Per Kilobase Million) or TPM (Transcripts Per Million) focus solely on sequencing depth. However, edgeR goes beyond that by considering the variations in library composition.
Different samples can have varying proportions of active genes, which can significantly impact the analysis results. To achieve accurate and reliable results, edgeR adjusts for both sequencing depth and library composition.
The Process of Library Normalization with edgeR
Let’s explore the step-by-step process of library normalization using edgeR:
Step 1: Removing Untranscribed Genes
The first step in library normalization is to remove all untranscribed genes, i.e., genes with zero read counts in all samples. This ensures that only relevant genes are considered in the analysis.
Step 2: Selecting a Reference Sample
Next, a reference sample is chosen to normalize all the other samples against. The reference sample acts as a baseline for comparison. It is crucial to select a sample that represents the average characteristics of the dataset to avoid biased results.
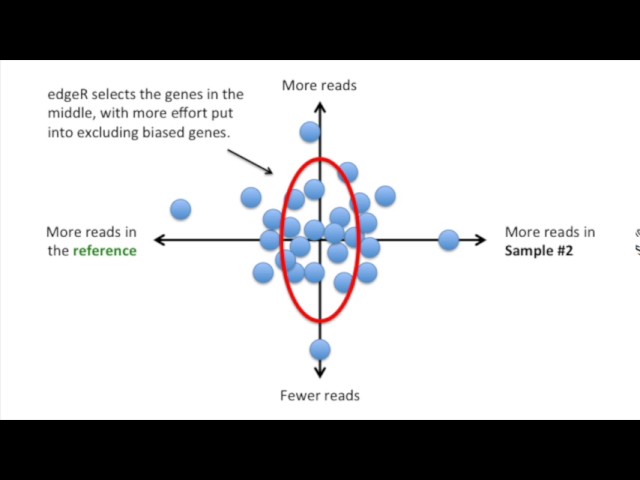
Step 3: Selecting Genes for Scaling Factors
edgeR calculates scaling factors separately for each sample relative to the reference sample. Different samples may use different genes to derive their scaling factors. Genes are selected based on their moderate read counts and unbiased expression levels.
Step 4: Calculating the Weighted Trimmed Mean of Log2 Ratios
Once the genes for scaling factors are selected, edgeR calculates the weighted average of their log2 ratios. Genes with higher read counts carry more weight, reducing the noise in the results.
Step 5: Converting Log2 Ratios to Normalized Scaling Factors
The weighted average of the log2 ratios is then converted back into normal numbers by raising it to the power of 2. These scaling factors reflect the adjustments needed to normalize the samples.
Step 6: Centering the Scaling Factors
To enhance the mathematical properties of the scaling factors, they are centered around 1 by dividing each raw scaling factor by their geometric mean. This step ensures the scaling factors are centered, providing a more stable and reliable normalization.
Now that you understand the step-by-step process of library normalization using edgeR, you can apply this knowledge to your genomic analyses. Remember, selecting the appropriate reference sample and genes for scaling factors play a vital role in achieving accurate results.
FAQs
Q: What is the significance of library normalization in genomic analysis?
A: Library normalization ensures accurate results in genomic analysis by adjusting for sequencing depth and variations in library composition. It enables fair comparisons between samples and improves the reliability of downstream analyses.
Q: Can edgeR be used with other normalization techniques?
A: Yes, edgeR can be used in conjunction with other normalization techniques. However, edgeR itself provides a comprehensive approach that takes into account both sequencing depth and library composition, reducing the need for additional normalization methods.
Conclusion
Library normalization plays a crucial role in genomic analysis, ensuring accurate and reliable results. edgeR’s unique approach, considering sequencing depth and library composition, provides a comprehensive solution for normalization. By following the step-by-step process outlined in this article, you can effectively normalize your genomic data using edgeR.
To learn more about edgeR and other exciting topics in technology, visit Techal. Stay tuned for our next article, where we’ll continue exploring the fascinating world of technology and its impact on various industries.


