Mobile networks may seem complex, but let’s simplify the 3G UMTS Network Architecture. In this article, we’ll break it down into easy-to-understand terms. So, let’s dive right in and take a look at the UMTS Network Architecture.
Understanding the Basics
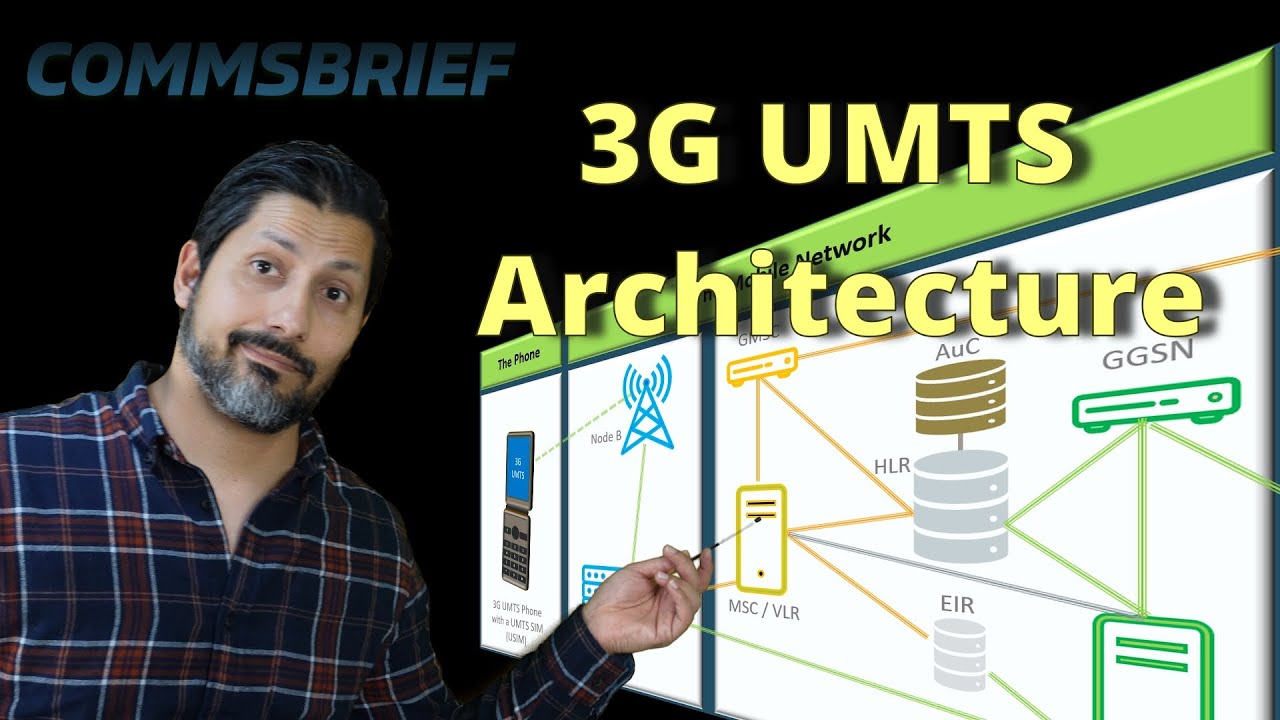
In a mobile network, we have a mobile phone, also known as a cell phone. Within the network, there are two main components: the radio network and the core network. The radio network consists of cell towers, known as nodeBs, and a Radio Network Controller (RNC). On the other hand, the core network serves as the brains of the mobile network.
The radio network acts as the arms and legs of a mobile network, providing the reach to connect to your phone wherever you are. Additionally, external networks connect the mobile network to telephone networks and the internet.
Simplified Network Diagram
To simplify the 3G UMTS Network Architecture, let’s remove the complexity of the network diagrams and focus on the network elements.
Starting from the left, we have the mobile phone, also called user equipment (UE), which uses a UMTS Subscriber Identity Module (USIM) card. Moving to the right, we have the radio network, consisting of the nodeB (cell tower) and the RNC, which together form the UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access Network (UTRAN).
Next, we have the core network, which includes various databases such as the Authentication Center (AuC), Home Location Register (HLR), and Equipment Identity Register (EIR). We also have the Mobile Switching Center (MSC) and Serving GPRS Support Node (SGSN) for circuit-switched and packet-switched services, respectively.
Finally, the outside world consists of networks like PSTN and ISDN for circuit-switched services, and the internet for packet-switched services.
Now that we have a clearer picture of the simplified network, let’s bring back the lines to see how the network elements are connected to each other.
The mobile phone communicates with the nodeB for any communication needs. The RNC controls multiple nodeBs and connects to the MSC for circuit-switched services like voice calls and text messages. It also connects to the SGSN for mobile internet services.
In the middle of the diagram, we have the databases. The AuC validates the SIM card and ensures secure connections. The HLR contains information about your home location and the services you can use. The EIR registers all the IMEI numbers on the network.
Understanding the combined GSM and UMTS Network Architecture is crucial as these networks coexist. GSM networks were not quickly replaced by 3G UMTS networks, and they continue to exist today. So whenever you see an “E” symbol on your phone, you are connected to the GSM network.
To fully comprehend the 3G UMTS Network Architecture, it is essential to see how it fits with GSM and the later generation, 4G LTE. In a separate video, we will cover the 4G LTE part of the architecture.
For more detailed information, check out our detailed post on this topic. Don’t forget to hit the like button and subscribe to our channel for new videos on technology topics.
FAQs
Q: What is the role of the radio network in a mobile network?
A: The radio network, consisting of nodeBs and an RNC, acts as the arms and legs of a mobile network, providing the reach to connect to your phone wherever you are.
Q: What are the databases in the core network?
A: The core network includes databases such as the Authentication Center (AuC), Home Location Register (HLR), and Equipment Identity Register (EIR).
Q: How does circuit-switching differ from packet-switching?
A: Circuit-switching establishes a dedicated communication link for the entire duration of the call, while packet-switching is more efficient as it sends data in packets, making it suitable for mobile internet or data services.
Conclusion
Understanding the 3G UMTS Network Architecture is essential for technology enthusiasts. By simplifying the network elements and their connections, we hope to empower you with knowledge about mobile networks. Remember to visit Techal for more insightful articles and videos on technology.


